This is an old revision of the document!
Image-Processing
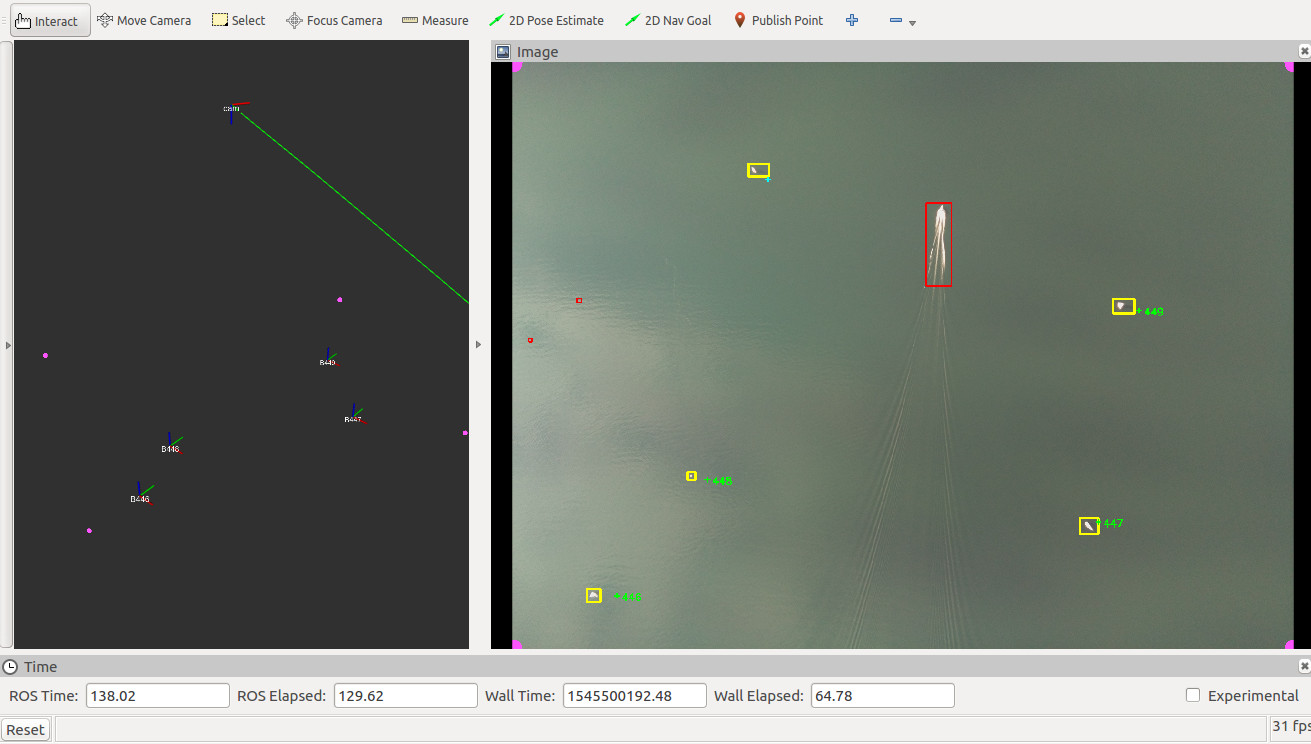
By analysing the image with we receive from the camera, we can detect boats on the sea. To achieve this, different algorithms and approaches from the image processing and deep learning domain can be used.
Detection by using edgedetector and a 2d tracker in world coordinates
Code
Algorithms
Assumptions for the algorithms
- By flying over the sea with 50-80km/h boats can be assumed to stand almost still in relation to the drone
- Waves appear and dissapear over time
- Approach to detect boats
- Detect parts in the image which dont change over time
- Redect parts by checking the same position in consecutive frames
- If parts look the same, save them
- If something is redetected over 3 frames, we can assume this could be a boat
Proposal / boat detector
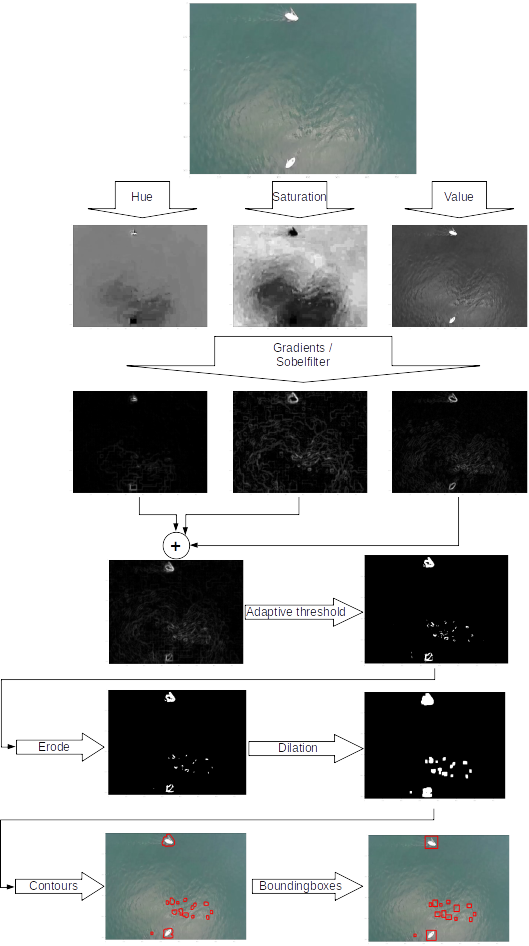
- Detection of randomly looking objects in the water
- Classical image processing ( no deep learning)
- Processing chain depicted in the image
- There false positives after inital detection
- Calculation of the 3D Position of the Objects
- In world coordinates
- By using a camera calibration
- Code optimized for ARM Platforms
- By using ARM related flags for OpenCV
- Alternative: Compute Library for even faster processing
- Runtime
- 0,8 sec @ 8 MegaPixel(3240×2480 Pixel) @ Raspberry Pi 3
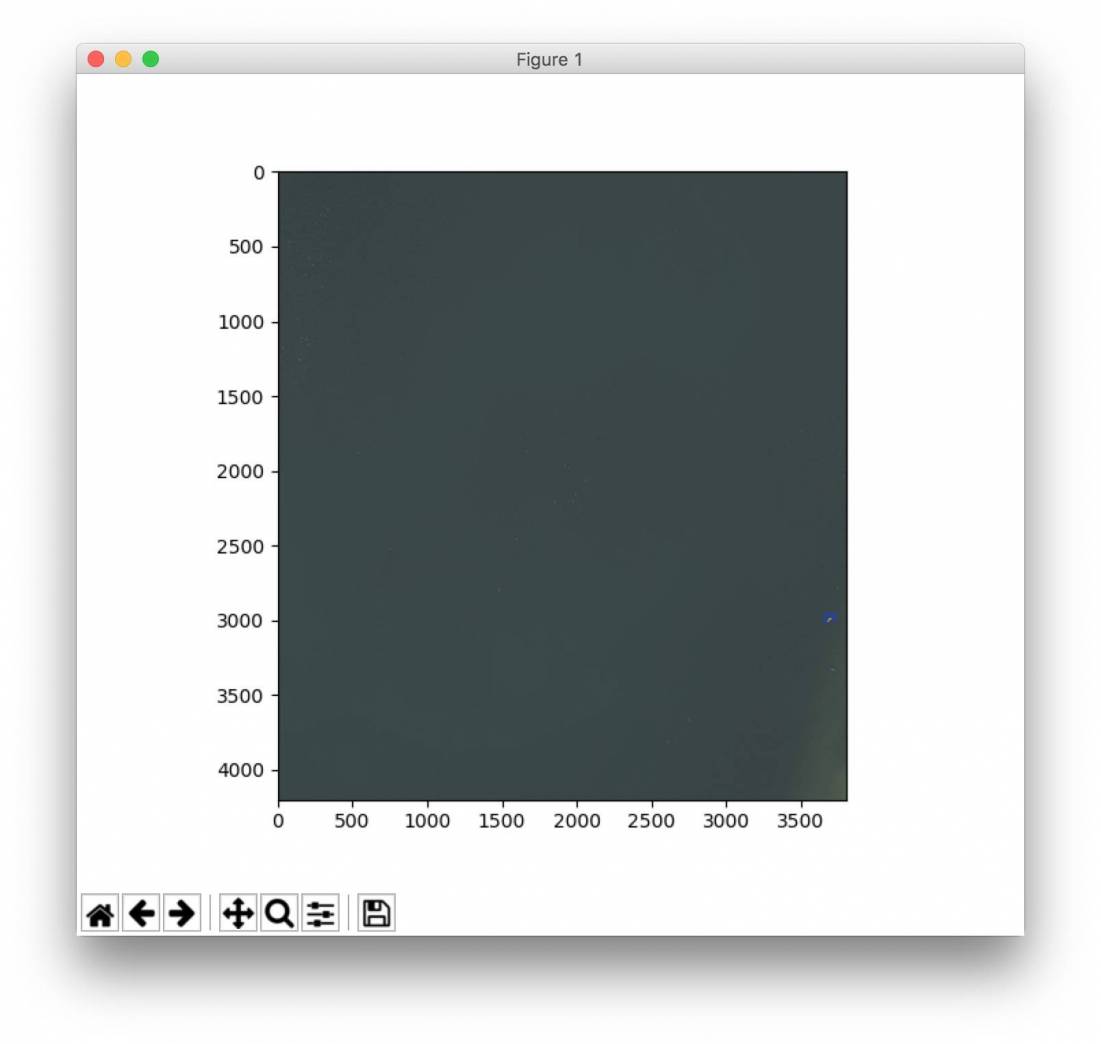
Tracking
- Redetect boats in consecutive frames
- Get more information/images about the same boats
- See image below
- Reduce false-positive rate
- Valid detections only if we redetect the same boat
- Algorithms
- Association Problem
- Euclidean distance based cost matrix between each possible track and detection
- Solve global neigherest neighbor assignement problem by using Hungarian Algorithm
- Tracking
- Different trackingmodels possible
- Constant position
- Kalman constant position
- Kalman constant velocity
Output
- Save boat images on harddisk
- Metadata for each detection is saved in exif-datablock of each detected boat
- GPS Position
- GPS Time
- Visualization of the detection in digikam
Used software
- ROS
- Module communication
- Coordinatesystem transformations
- Recording and playback of datasets
- Visualisation
- MAVROS
- Communication with the drone via MAVLINK
- OpenCV
- Imageprocessing
- ARM Compute Library
- Imageprocessing
Outlook
- Deep Learning
- Test different approaches
- Runtime evaluation for embedded hardware
- Interfaces to send detections via MAVLINK to basestation
Presentation on the topic
Imagerecognition by using a OpenCV Haar Cascade Classifier
I composed a few images to train a Haar Cascade Classifier. The code is over here:
https://git.etech.fh-augsburg.de/friedrich.beckmann/bilderkennung
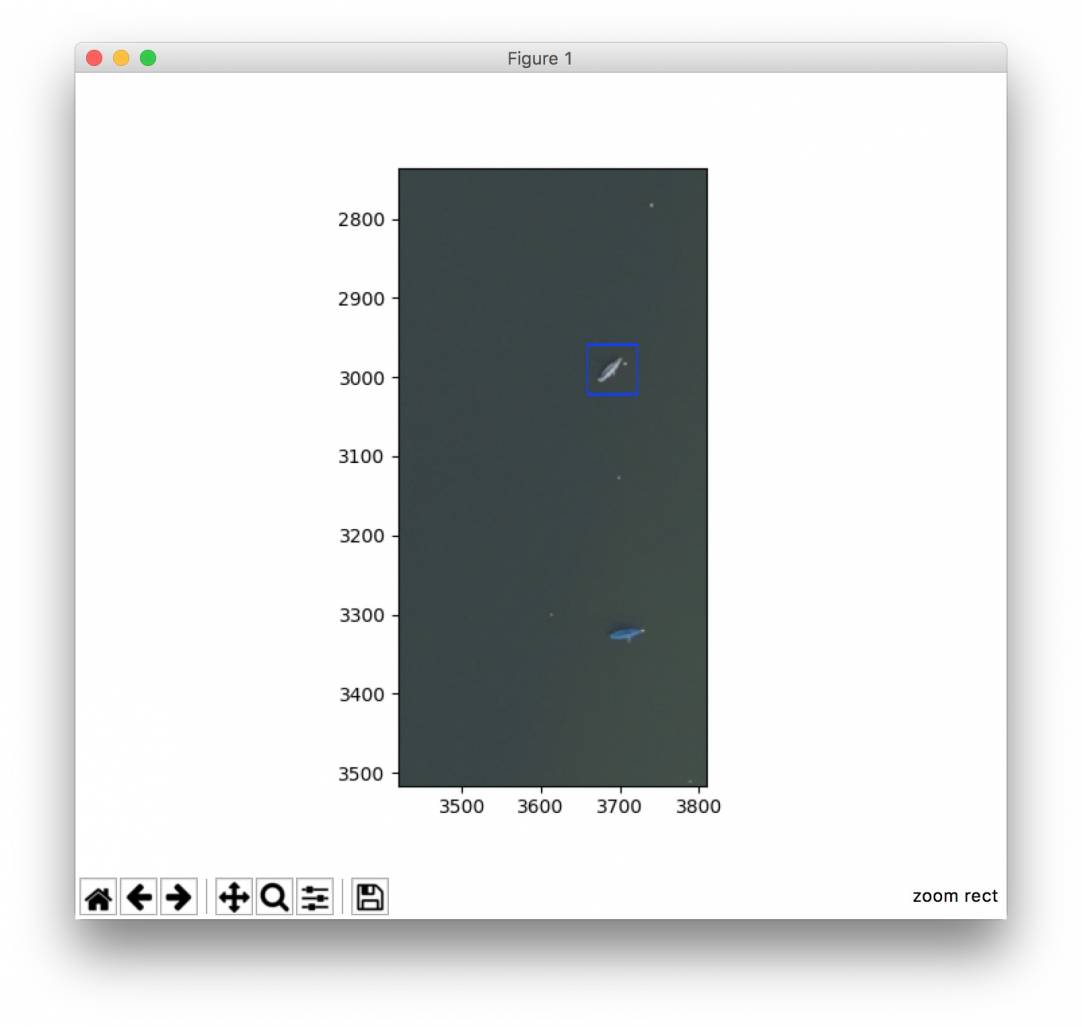
The detected boats can be seen in the following image. They are marked by a blue rectangle.
Recified:
In this example the second boat with Persenning does not get detect. The boat above get detected.
Datasets
For development and test purposes we need datasets. So far we got these datasets:
- We got access to the Seagull Dataset
Kamera kalibrieren (intrinsisch)
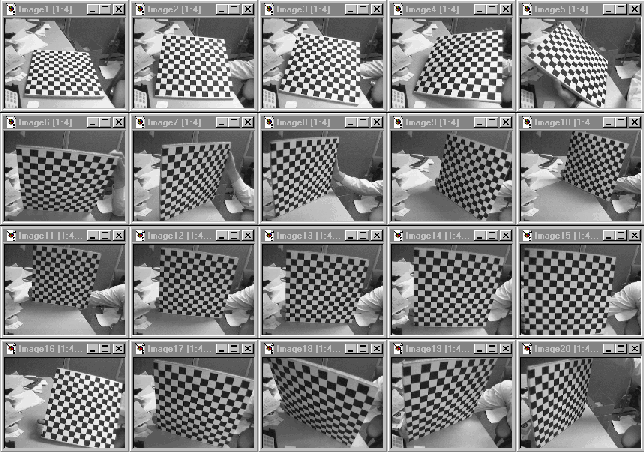
Um eine Kamera zu kalibriern muss ein Kamera Kalibrier Muster vor die Kamera gehalten werden in unterschiedlichen Positionen und jeweils ein Bild aufgenommen werden. Mithilfe der Bilder können dann die Eigenschaften / Intrinsischen Parameter berechnet werden. Dazu zählen zum Beispiel die Brennweite und Verzerrungsparameter der Kamera. Mithilfe der Parameter können dann prinzipiell 3D Punkte aus einem Kamerabild berechnet werden, die Tiefeninformation fehlt hierfür aber natürlich.
Schritt für Schritt Anleitung
- Download und Ausdruck des Musters.
- Wichtig ist das das Pattern so groß wie möglich ausgedruckt wird
- Befestigung ohne Wellen auf einer steifen Unterlage
- Länge einer Zelle ausmessen. Die Größe wird später bei der Berechnung der Kalibrierung benötigt.
- Kamera fest aufstellen aufstellen, sodas man davor etwas Platz hat
- Kalibrierbilder erstellen
- Das Muster aus verschiedenen Winkeln in die Kamera halten
- Das Muster muss in jedem Bild vollständig zu sehen sein
- Das Muster muss grob jeden Teil des Kamerabildes mehrmals erfassen
- Das Muster darf muss scharf abgebildet werden - Bewegung vermeiden bei der Bildaufnahme um keinen Motionblur zu ereugen
- Das Muster darf nicht über 45° gekippt werden, sodass im Bild die Reihen und Spalten eindeutig unterscheidbar sind anhand der Anordnung
- Wichtig ist das die Auflösung der Bilder in der gleichen Auflösung erfolgen muss, in der man die Kameradaten letztendlich verwenden möchte
- Wichtig ist möglichst Kompressionsfreie Bilder aufzunehmen um Artefakte zu unterbinden, welche Kalibrierfehler erzeugen
- Praktische Hinweise für Raspberry Pi
- Videoaufnahme nicht verwenden, da dort starke Komprimierung verwendet wird
- Serienbildfunktion nutzen
- Manuelles Triggern der Kamera
- Aufnahme mittels ROS Toolchain möglich - verharren in jeder Lage für ca. 3 Sekunden
- Berechnung der Kalibrierung
- Tools
- Mittels MATLAB Tool: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g8SyzR0jZOA
- Mittels OpenCV Sample Code Tool:
- Konfiguration der Inputbilder als XML file
- Starten des Kalibriervorgangs indem man die executable in
samples/cpp/tutorial_code/calib3d/camera_calibration/mit dem XML file als parameter aufruft
- Der berechnete mittlere Fehler (RMS) der Kalibrierung sollte sich im Bereich < = 1 Pixel bewegen